STPM Trial Question
7. Every project should carry out five phases of systems
development life cycle (SDLC) which are planning, analysis, design,
implementation and maintenance.
a) Explain why the planning phase is important in SDLC.
The aim of planning phase is to determine the needs of
developing a new information system. In this phase, the system analyst (with
the cooperation of the customer) investigates the current or existing system to
get right information. It is because without right information it is not possible
to develop a good system.
b) Briefly explain five documentations delivered from the
planning phase in SDLC.
1. Economic feasibility – measures whether the lifetime
benefits of the proposed information system will be greater than its lifetime
cost.
2. Technical feasibility – measures whether the company has
or can obtain the hardware, software, and people needed to deliver and then
support the proposed information system.
3. Operational feasibility – measures how well the proposed
information system will work.
4. Social feasibility – measures whether the proposed system
can be accepted by the society.
5. Legal feasibility – measures whether the proposed system
violate the laws of the country or not.
6. Schedule feasibility – looks at how long the system will
take to develop, or whether it can be done in a desired time-frame.
c) State five consequences of not performing the planning phase correctly.
1. Not understanding the environment or focusing on results.
2. Partial commitment.
3. Not having the right people involved.
4. Unwillingness or inability to change.
5. Ignoring marketplace reality, facts, and assumptions.
6. No accountability or follow through.
7. Unrealistic goals or lack of focus and resources.
1. Corrective maintenance – maintenance performed to repair
an error in system design.
2. Perfective maintenance – system maintenance performs to
improve a computer program.
3. Adaptive maintenance – maintenance to add new features
based on user feedback by modifying or extending the existing information
system.
4. Preventive maintenance – maintenance aimed at the
prevention of future breakdowns and failures.
5. Assess system security – responsible for ensuring the
security of the system to protect the information system against all types of
threats.
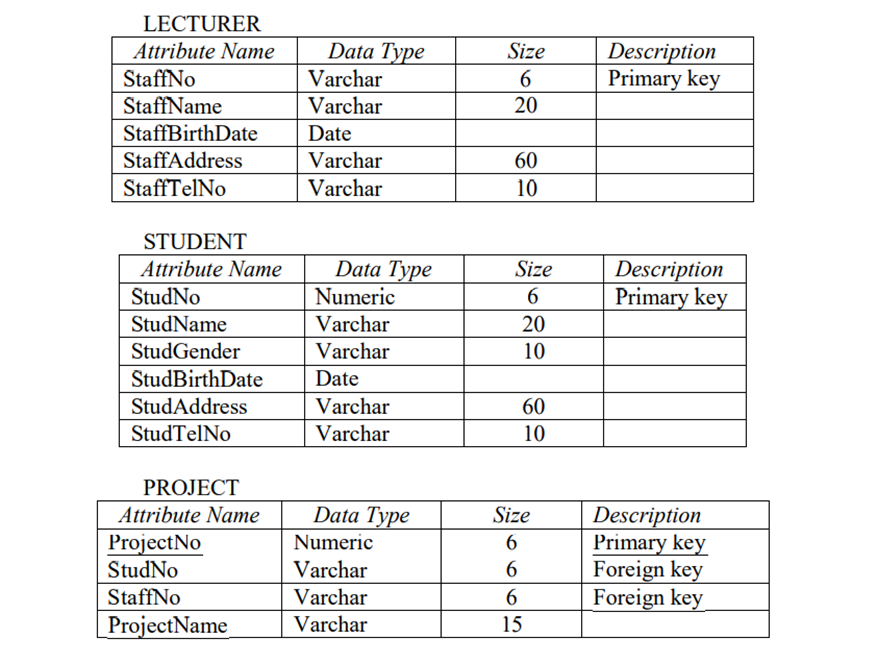
8. An information systems project of a college consists of
three tables which are shown below.
Write SQL expressions for the following queries:
a) Create a table for PROJECT.
CREATE TABLE PROJECT (
ProjectNo INTEGER
NOT NULL UNIQUE,
StudNo VARCHAR (6) NOT NULL,
StaffNo VARCHAR (6) NOT NULL,
ProjectName VARCHAR (15),
PRIMARY KEY (ProjectNo, StudNo,
StaffNo));
b) List all female students in the college.
SELECT *
FROM STUDENT
WHERE StudGender = ‘Female’;
This is because:
1. Company is running two systems at the same time to
accomplish the same tasks.
2. Creates a doubling of time and materials for the users.
3. Running both systems might place an extra burden on the hardware, which can
cause processing delays.
5. The conversion of an old information system to a new
system involves four options of strategy such as direct, parallel, pilot or
phased implementations. Identify and describe the most expensive conversion
strategy of the information system. Justify your choice.
ANS: Parallel conversion approach – Parallel operation
conversion methods generally tend to be the most expensive. This method
requires that both the old and new systems be run parallel for a specific
period of times. Users must work fully in both systems to reap the benefits of
a parallel conversion. This method is more expensive but it is the least risky.
STPM 2019 Trial 3rd
1. Give two reasons for system developers to involve users
in a system development process.
a) Users are people who use the system; so the users provide
information about the detailed function and operations needed in the system
development process.
b) If the system is to be successful, the user must be
included in all stages of system development; users are more apt to accept the
system if they involve to in a system development process.
2. The systems analyst of a retail company has been
requested to conduct a feasibility study to introduce a new inventory control
system. The function of the inventory control system is to manage the quantity
of goods in stock based on demand of customers.
a) Explain two purposes of feasibility study.
- The feasibility of a project can be ascertained in terms
of technical factor, economic factor or both. A feasibility study is documented
with a report showing all the specifications of the project.
- The feasibility study is used to determine if the project
should proceed. If the project is to proceed, the feasibility study will
produce a project plan and budget estimates for the future stages of
development.
b) Describe two categories of feasibility study which are
related to the inventory control system.
i. Technical Feasibility - Technical feasibility refers to
the ability of tile process to take advantage of the current state of the
technology in pursuing further improvement. The technical capability of the
personnel as well as the capability of the available technology should be
considered. Technology transfer between geographical areas and cultures needs to
be analysed to understand productivity loss (or gain) due to differences.
ii. Economic Feasibility - This involves the feasibility of
the proposed project to generate economic benefits. A benefit-cost analysis and
a breakeven analysis are important aspects of evaluating the economic
feasibility of new industrial projects. The tangible and intangible aspects of
a project should be translated into economic terms to facilitate a consistent
basis for evaluation.
iii. Legal feasibility - determines whether there is any
conflict between the proposed system and legal requirements - for example, will
the system contravene the Information Privacy Act.
iv. Operational feasibility - Operational feasibility is
concerned with whether the current work practices and procedures are adequate
to support the new system. It is also concerned with social factors - how the
organizational change will affect the working lives of those affected by the
system.
v. Schedule feasibility - looks at how long the system will
take to develop, or whether it can be done in a desired time-frame.
No comments:
Post a Comment